Climate Zone Map Of Africa – Climate zone of Africa, showing the ecological separation between the Sahara (red), the temperate semi-arid climate of the Sahel (orange), and the tropical climate of Ctral and West Africa (blue). Southern Africa is transitioning to tropical and subtropical climates (green and yellow) and more desert or semi-arid regions, centered on Namibia, Botswana and South Africa.
African climate is a type of climate such as tropical climate, wet and dry climate, subtropical climate, tropical monsoon climate, semi-arid climate (semi-desert and grassland), desert climate (very dry). and dry). and the climate of the equatorial plateau. Warm weather is rare throughout the continent, except at the highest elevations and along the border. In fact, Africa’s climate is more variable with rainfall and temperatures consistently higher. The African Sahara is the sunniest and driest part of the continent due to the spread of tropical mountains with hot and dry air masses. Africa holds many heat records: the continent has the hottest areas throughout the year, the hottest summer weather, the highest solar eclipses, and more.
Climate Zone Map Of Africa

Due to its location across the equator and subtropics, both the northern and southern hemispheres, Africa has a variety of climates. The continent is mostly located in the intertropical zone between the Tropics of Cancer and the Tropics of Capricorn, which is surprisingly humid. The rain is always high and the weather is hot. A hot and humid climate covers all of Africa, but most of the northern regions are characterized by dryness and high temperatures. Only the northernmost and southernmost parts of this continent have a Mediterranean climate. The equator passes through the center of Africa as well as the Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn, making Africa the most tropical continent.
Africa On Track To Contribute To Majority Of Global Particulate Matter
Globally, global warming near the equator leads to strong winds and winds along the monsoon or tropical transition zone. Turning the trough near the equator causes the wind to rise and move away from the equator. As it moves toward the midlatitudes, the wind cools and sinks, resulting in weakening near the 30th parallel in both hemispheres. This circulation is known as the Hadley cell and leads to the formation of tropical mountains.
And it is the coldest throughout the southern hemisphere and in the highlands in the eastern and northwestern parts of this continent. The warmest average temperature on Earth is in Dalol, Ethiopia, with an average annual temperature of 33.9 °C (93.0 °F).
The hottest temperature ever recorded in Africa was 57.8 °C (136.0 °F) in Aziziyah, Libya on September 13, 1922. The second is incorrect due to incorrect thermometer readings. . The hottest place in the world is Death Valley in California.
The temperature difference, along with temperature and humidity effects along the Red Sea coast of Eritrea and the Gulf of Ade, Somalia, ranged between 57 °C (135 °F) and 63 °C (145 °F) during the afternoon.
File:africa Map Of Köppen Climate Classification.svg
However, significant parts of Africa experience extreme heat during many years of the year, especially semi-deserts, deserts, grasslands, and grasslands. The African Sahara is the hottest place on Earth, especially the Sahara Desert and the Danakil Desert in the Horn of Africa.
The East African low-level air current is considered to play an important role in the southwest African monsoon.
And it helps create tropical waves that cross the tropical Atlantic and eastern Pacific in the summer.

This plane exhibits both barotropic instability and baroclinic instability, which produce synoptic-scale disturbances that propagate westward in planes known as African or tropical waves. A few mesoscale systems embedded in these waves develop into tropical cyclones after moving from West Africa to the Atlantic Ocean, mainly in August and September. Tropical storm formation is suppressed when the plane is normally positioned in the south during the peak months of the Atlantic hurricane season.
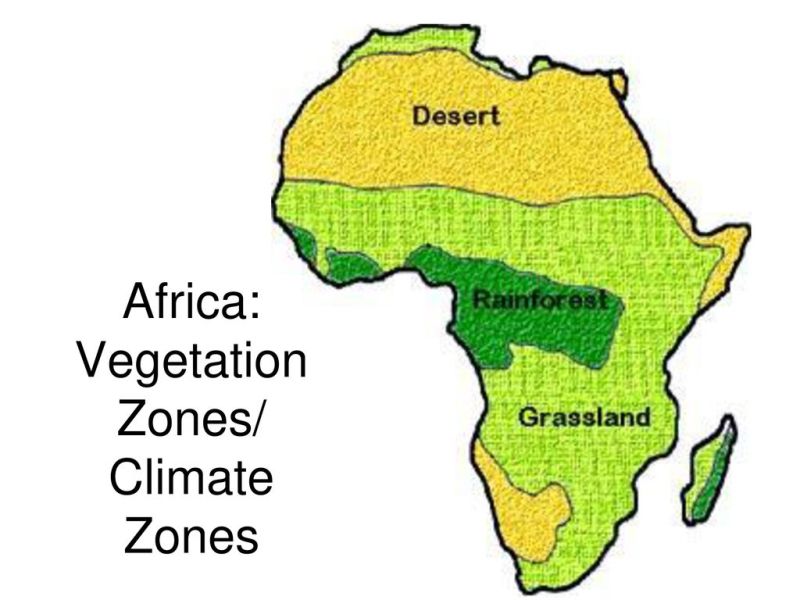
Africa: Climate Zones
Large parts of North and South Africa, as well as the entire Horn of Africa, have predominantly hot desert or semi-arid and hot to humid climates. The Sahara Desert in North Africa is the hottest desert in the world and the hottest, driest and sunniest place on Earth. In the southern part of the Sahara there is a narrow semi-desert grassland (semi-arid zone) called the Sahel, while the southernmost part of Africa consists of savannah plains and the central part is dense forest. rain forest. The equator near Convergce is the wettest part of the continent. Every year, rain belts across the continent move north to sub-Saharan Africa in August and cross south to South Africa in March.
El Nino produces drier-than-normal conditions in southern Africa from December to February and drier-than-normal conditions in equatorial East Africa during the same period.
In Madagascar, strong winds blew in the eastern part of the island and brought drier winds to the south and west, leaving the western part of the island in shadow. Rain. This resulted in more rainfall in the northeastern part of Madagascar than in the southwestern part.
South Africa receives most of its rainfall from summer convective storms and extratropical storms across the westerlies. Once a decade, a tropical storm brings heavy rainfall across the region.
No Plain Sailing For Marine Life As Climate Warms (constantine Alexander’s Journal)
Snow occurs almost annually in some South African mountains, including the Cederberg Mountains and around Ceres, the South Western Cape and Draxberg in Natal and Lesotho. Tiffdell Resort in Draksberg is the only commercial ski resort in South Africa with “advanced snowmaking capacity” that allows skiing for three months of the year.
From the University of Cape Town, both equipped with ski huts on the Hex River. Skiing, including ice skating in the Cape, is interesting both in terms of when it snows and when there is enough snow to cover the cliffs.
Table Mountain gets a little snow on the front table and Devil’s Peak every few years. Snowfall occurred on Table Mountain on September 20, 2013.

Snow is a rare occurrence in Johannesburg. It fell in May 1956, August 1962, June 1964, September 1981, August 2006, and June 27, 2007.
Sub Saharan Africa
In addition, regular snowfall in the Atlas Mountains in the West. Snowfall is also common on Mount Kia and Mount Kilimanjaro in Tanzania.
There is a permanent glacier on Mount Rwzori on the border of Uganda and the Democratic Republic of Congo. However, by the 2010s the glacier had shrunk and was threatened with extinction due to rising temperatures.
This graph shows temperature changes in Africa between 1901 and 2021, with red being warmer and blue being colder than average (the average temperature in 1971-2000 was defined as the border between blue and red).
Climate change in Africa is an increasingly serious threat in Africa, which is among the continents most vulnerable to the effects of climate change.
The Soil Maps Of Africa
This vulnerability is caused by several factors, including poor adaptation, declining commodity prices, underdeveloped livelihood ecosystems, and agricultural production systems.
Climate change risks to agricultural production, food security, water resources and ecosystem services are likely to further impact livelihoods and prospects for sustainable development in Africa.
With high confidence, it was predicted by the IPCC in 2007 that in many African countries and regions, agricultural production and food security may be severely compromised by climate change and climate change.

This risk management requires the integration of mitigation and adaptation strategies in the management of environmental goods and services and agricultural production systems in Africa.
What Do You Know About It?
Over the next few decades, climate change-induced global warming is projected to occur over nearly all of Earth’s surface, and global average precipitation will increase.
In fact, Africa is warming faster than the global average. Much of the continent may become uninhabitable due to the rapid effects of climate change, which will have catastrophic effects on human health, food security and poverty.
Local effects on tropical rainfall are expected to be more variable and signs of change at a location less clear, although changes are expected. Consistent with this, observed surface temperatures in Africa increased strongly from the late 19th century to the early 21st century, by about 1°C, but locally up to 3°C for minimum temperatures on the d dry season coast.
For example, Kia is very vulnerable to the effects of climate change. Major climate risks include droughts and floods, with projects predicting more and less rainfall. In addition, other forecasts predict a temperature increase of 0.5 to 2 degrees Celsius.
A Hand Painted Map Of Africa Depicting Climate Zones, Debre Berhan, Ethiopia Stock Photo
In densely populated urban settlements in Nairobi, Kenya, informal settlement conditions or “slums” can exacerbate climate change impacts and disaster risks.
In particular, a large informal lifestyle often creates
Us climate zone map, usda climate zone map, colorado climate zone map, sunset climate zone map, florida climate zone map, climate zone map of usa, plant climate zone map, climate zone of africa, climate zone map australia, climate zone map, climate zone map california, world climate zone map