Physical Map Of Africa With Rivers And Mountains And Deserts – Description: A detailed map of Africa that shows major features such as elevations, mountains, deserts, lakes, rivers, plains, plains, forests, other areas with forests or forests, landforms and other color features.
The second largest and second most populous continent in the world, Africa covers an area of approximately 30 million square kilometers, including neighboring islands. It covers 6% of the total area and 20% of the total area.
Physical Map Of Africa With Rivers And Mountains And Deserts

This represents 15% of the world’s population. Africa is surrounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Suez Canal and the Red Sea to the northeast by the Sinai Peninsula. It has the Indian Ocean to the southeast and the Atlantic Ocean to the west. Inland there are various islands. It has 54 recognized independent states.
Africa Physical Map Rivers And Bodies Of Water Diagram
The most interesting thing about Africa is that its population is the smallest among all continents. It is separated from Europe by the Mediterranean Sea and is connected to Asia in the northeast by the Isthmus of Suez.
The extreme north is Ras ben Sakka in Tunisia and the extreme south is Cape Agulhas in South Africa. The distance between these two points is about 8000 km. Africa’s coastline is very long: about 26,000 kilometers. The largest country in Africa is Algeria, and the smallest country is the Seychelles, a group of islands in the east.
The following deserts exist in Africa: the Sahara desert (in North Africa), the Kalahari desert (in the south). The Atlas Mountains are located in Algeria, Morocco and Tunisia. Mount Kilimanjaro is the highest mountain in Africa. Other mountains found in Africa are Mount Mitumba and Mount Ahaggar. The African transition zone divides North Africa from the rest of Africa due to climate and culture. Cultural conflicts and desertification are common in this area. The dry, arid type B climate, found in the Sahara desert, is located in the northern part of the region. In the southern part of the region, a tropical type A climate prevails. Global climate change continues to change the continent. The shifting sands of the Sahara slowly move south to the tropics. Desertification in the area continues as the environment and human activities are failing in the area due to overgrazing and lack of rain. Type B seasons also occur in the southern subtropics. The Kalahari and Namibian deserts are located in South Africa, especially in the countries of Botswana and Namibia.
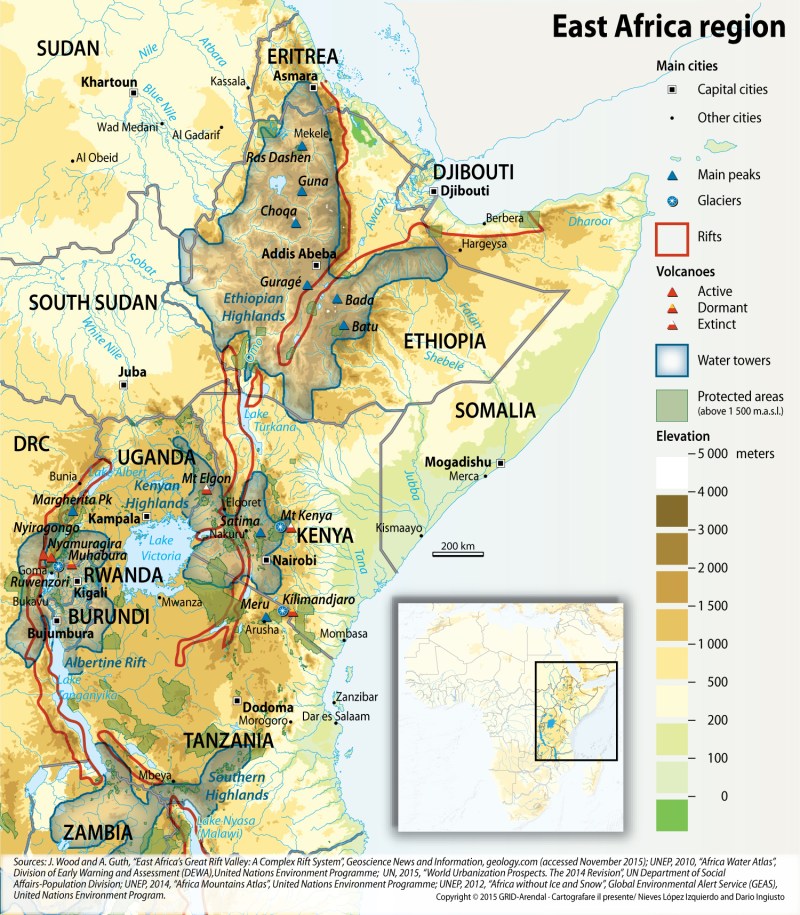
For a continent as large as Africa, sub-Saharan Africa does not have the same high mountain ranges as North or South America, Europe, Asia or Antarctica. However, in the highlands of Ethiopia there is Mount Ethiopia, which reaches 15,000 meters. In East Africa there are several well-known peaks of high-altitude volcanoes. The highest point in Africa, Mount Kilimanjaro in Tanzania near the Kenyan border is 19,340 feet. Mount Kenya near Kenya is 17,058 meters high. The Rwenzori Mountains on the Congo-Uganda border rise to more than 16,000 meters and are responsible for the destruction of the area. Permafrost exists in these regions, even though they are close to the equator. To the west of the continent is Mount Cameroon in Central Africa at over 13,000 meters. The Cape Ranges of South Africa are low mountains not exceeding 6,000 feet in height. The continent of Africa consists of basins and mountains without high mountains. Plateaus can reach over 1,000 to 2,500 feet. The only continuous feature is the eastern plains that cross the tectonic plate boundary from the Red Sea to South Africa.
Sudan Physical Map
The major rivers in Africa are the Nile, Niger, Congo and Zambezi. The Nile competes with the Amazon to be the world’s longest river; The White Nile originates from Lake Victoria in East Africa and the Blue Nile originates from Lake Tana in Ethiopia. The Niger River flows through western Africa; his mouth is in Nigeria. The Congo River crosses the equator in a very tropical region, which makes the water flow slower than the Amazon. The Zambezi River in the south is famous for the huge Victoria Falls on the border of Zambia and Zimbabwe. Victoria Falls is considered to be the largest waterfall in the world. There are other important rivers, such as the Orange River, which forms part of the border between South Africa and Namibia.
South of the Sahara in Africa there are several large lakes. The largest lake is Lake Victoria, which borders several East African countries and is considered the second largest lake in the world in terms of area. Only Lake Superior in North America has a larger area. To the east of the Rift Valley are several large lakes. The three largest lakes on the west bank are Lake Malawi, Lake Tanganyika, and Lake Albert. To the north-east of Kenya is Lake Turkana, which reaches the border with Ethiopia. Lake Chad is located in the transition zone of Africa on the border of Chad, Mali and Nigeria. Lake Chad has dropped significantly in recent years.
The Equator runs through the middle of sub-Saharan Africa, giving it a tropical climate type A. These areas tend to receive a lot of rain, which results in light soils that don’t work as well as areas with fertile volcanic soil, such as found in plains. Root crops are common in Africa, as are millet and maize (maize). The eastern and southern parts of the savanna experience rainfall that affects the growing season. Soils in savanna areas are often infertile and cannot be relied upon to meet the agricultural needs of growing populations. Savannas are generally grasslands or scrubby forests with seasonal rainfall. Cattle and livestock grazing is common in the rangelands, and migration is frequent depending on the grazing season. Some areas in South Africa have large agricultural activities in the C season. However, the northern part of the world in sub-Saharan Africa does not have many fertile areas. People who are increasingly engaged in agriculture have always depended on the land for food and sustenance, but these conditions do not bode well for the future of Africa. The population is growing faster than the growth of agriculture.

Population growth in sub-Saharan Africa is making the environment tax free. When the carrying capacity is exceeded, natural costs decrease at an unsustainable rate. Deforestation occurs in areas where wood is needed the most, and trees are cut down faster than they can grow back. Overpopulation is also disrupting the biodiversity that the African continent is known for. Large animals such as rhinos, elephants and lions have been poached or killed with devastating consequences. The creation of zoos and game reserves has brought the problem to an end, but poaching remains a serious problem even in these protected areas. The populations of gorillas and chimpanzees have also been stressed by overpopulation. People kill these animals for wildlife and human activities reduce their habitat.
A Humid Corridor Across The Sahara For The Migration Of Early Modern Humans Out Of Africa 120,000 Years Ago
An Introduction to World Regional Geography by R. Adam Dastrup, MA, GISP is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License unless otherwise noted. The physiography of Africa basically reflects the history of geology and geology that has been described in the previous section. The continent consists of small mountains in the Atlas Mountains in the northwest and the Cape Ranges in the south. Between these mountains there are several mountains, with large areas of flat or slightly sloping, and sometimes made of a lot of hard and hard rock. The area is surrounded by a belt of steep mountains, at the bottom of which there are coastal belts running along the Mediterranean Sea, along the coast of Tanzania and Mozambique, a narrow belt between the rivers Niger and Cunene (Kunene), and a region in the north of Gambia. and Senegal. rivers.
Kilimanjaro (5,895 meters) is the highest point in the world; the lowest is Lake Assal (157 meters below sea level) in Djibouti. Relative to its size, Africa has fewer high mountains and fewer plains than any other continent. A few areas above 8,000 feet are mountain peaks or mountains. All land below 500 feet is within 500 miles of the coast, except for two small basins in the Sahara.
The high areas in the south and east are very different from the low areas in the west and north of the continent. South of a line from the mouth of the Congo River to the Gulf of Aden, most of the land is 1,000 meters or more above sea level, and many exceed 3,000 and even 4,000 meters. North of this line is a little above 3,000 feet,
Map of africa and rivers, map of china with rivers mountains and deserts, physical map of south africa with rivers and mountains, map of africa with rivers and mountains, physical map of africa with rivers and mountains, physical map of africa with rivers and mountains and deserts pdf, physical map of india with rivers mountains and deserts, india map with rivers and mountains, physical map of asia with rivers mountains and deserts, world map with rivers and mountains, us map with rivers lakes and mountains, africa map with rivers and deserts