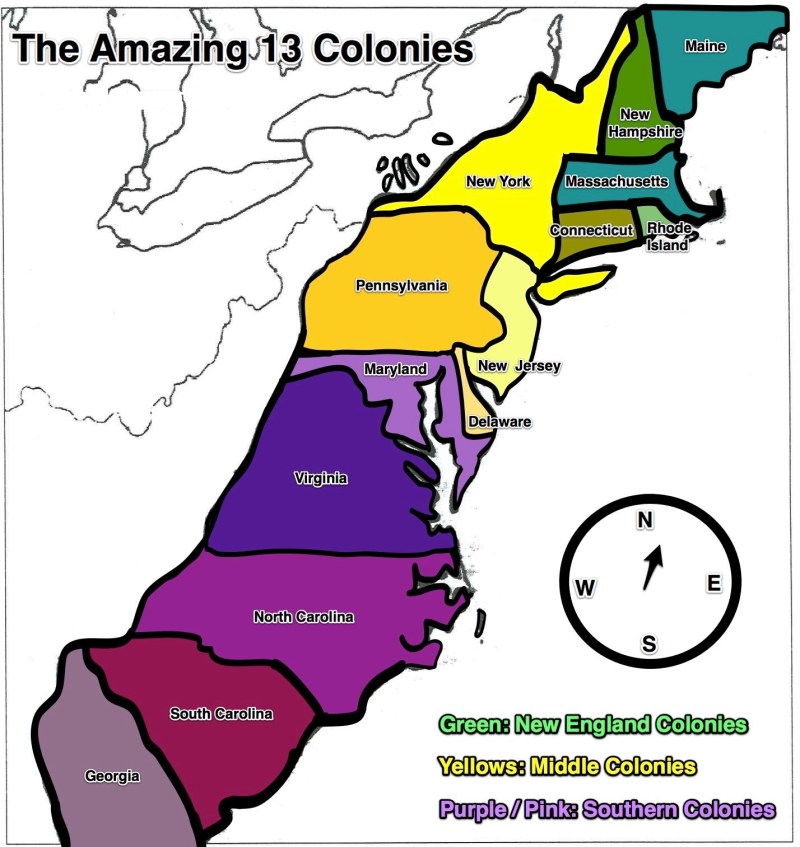
Map Of The 13 Colonies – Can your students find the 13 colonies on the map? In this simple lesson, students will learn the names and locations of the 13 colonies. They also locate the colonies in the regions: New England, Middle and South.
1. Learn about the world location of the 13 American colonies with the help of the video. Get links to my five favorite 13 Colony videos here.
Map Of The 13 Colonies

2. Show students a modern map of the United States like this one. Seek from them 13 colonies.
The Thirteen Colonies Map
Name the states that were originally 13 colonies. Know the territories around the colonies (eg: Atlantic Ocean to the east, Canada to the north, Florida to the south etc.).
You can assume that the students know the location of the 13 colonies, and some do. But chances are many don’t!
In this lesson, students place the colonies in time so that the colonies are established. They will also learn who founded each colony and the causes.
This activity includes business cards that will get your students out of their seats! I also included a review of the old paper endings. This is a great number 13 Colony Map Sheet.
Map Showing Land Claims Of The Thirteen Original States 1783. Color Lithograph Stock Photo
If you need more help with 13 Colonies, my 3-week unit is used by thousands of teachers and is one of the sales resources. Your students will love the Jacobtown simulation where they make decisions that will determine their survival.
Enter your email address now to read and receive free resources and information about the Civil War! Traditionally, when we tell the story of the “Colonies of America,” we’re talking about the English colonies along the east coast. This history is incomplete – at the time when the English began to seriously establish colonies, there were many French, Spanish, Dutch, and even Russian colonial stations on the American continent, but the history of these 13 colonies (New Hampshire, Massachusetts, Connecticut). (Rhode Island, New York, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, Delaware, Maryland, Virginia, North Carolina, South Carolina and Georgia). These were the colonies that merged into the United States of America.
The sixteenth century in England was a turbulent place. Because they can make more money selling wool than selling meat, many farmers have turned their fields into pasture for sheep. Hence the scarcity of food; and at the same time many lost their agricultural labors.

The 16th century was also a time of mercantilism, a highly competitive economic philosophy that encouraged European nations to acquire as many colonies as possible. As a result, most of the English colonies in North America were commercial enterprises. They gave an end for England’s surplus population and (in some cases) more religious freedom than England, but their main purpose was to get money for sponsors.
Map Of The American Colonies
In 1606, King James divided the Atlantic coast into two parts, distributing the southern part to London (after the Virgin Company) and the northern part to the Plymouth Company.
The first English settlement in North America was established about 20 years ago, in 1587, when a group of colonists (91 men, 17 women and nine children) led by Walter Raleigh settled on Roanoke Island. By the 1590s, the Roanoke colony had completely disappeared. Historians do not yet know what happened to the inhabitants.
In 1606, a few months after James published his paper, the London Company sent 144 men to Virginia with three ships: the Godspeed, the Discovery, and the Constant Susanna. They reached the Chesapeake Bay in the spring of 1607 and traveled about 60 miles to the James River, where they established a settlement they called Jamestown.
The colonists of Jacobopolis had a difficult time: they were so industrious looking for gold and exportable wealth that they could hardly feed themselves. It was not until 1616, when Virginia colonists learned to grow tobacco, that the colony seemed likely to survive. The first African slave came to Virginia in 1619.
The Thirteen Original Colonies In 1774
In 1632 the English crown granted approximately 12 million acres of land on the upper Chesapeake Bay to Cecil Calvert 2nd Lord of Baltimore. This colony, which was named Queen Maryland, was in many ways similar to Virginia. Its owners grew tobacco in large plantations that depended on the labor of indentured slaves and indentured servants.
But unlike the founders of Virginia, Lord Baltimore was Catholic and hoped that his colony would be a refuge from co-religious persecutors. Maryland is known for its policy of religious tolerance.
The first English immigrants to the New England colonies were a small group of Puritan separatists, later called pilgrims, who arrived in Plymouth in 1620 to found Plymouth Colony. Ten years later, a wealthy syndicate known as the Massachusetts Bay Company sent a much larger (and more liberal) group of Puritans to found another settlement in Massachusetts. With the help of the local natives, the settlers soon learned to farm, fish, and hunt, and prospered in Massachusetts.

As Massachusetts grew, they established new colonies in New England. Puritans who thought Massachusetts was not pious enough formed the colonies of Connecticut and Newport (both joined in 1665). Meanwhile the Puritans, who found Massachusetts too restrictive, established the colony of Rhode Island, where all, including the Jews, “had full freedom in religious matters.” North of the Massachusetts Bay Colony, some adventurous settlers formed the New Hampshire Colony.
Colonies Map Coloring Page
In 1664, King Charles II granted to his brother James, Duke of York, the territory between New England and Virginia, the largest of which was already well-known by Dutch merchants and proprietors. The English soon occupied New Netherland with the Dutch and named it New York.
Most of the Dutch (as well as Belgian Flemish and Walloons, French Huguenots, Scandinavians and Germans) settled there. This made New York one of the most diverse and prosperous colonies in the New World.
In 1680, the king granted 40 square miles of land west of the Delaware River to William Penn, a Quaker who owned large tracts of land in Ireland. Penn’s North American possessions became the colony of “Penns Woods” or Pennsylvania.
Invited by the fertile soil and religious tolerance that Penn promised, people migrated from all over Europe. Like their Puritan counterparts in New England, most emigrants paid off their colonies, were not indentured slaves, and did not have enough money to settle when they arrived. For this reason Tarentum soon became a prosperous and equal second place.
Original 13 States
In contrast, the Carolina colony, the territory south from Virginia to Florida and west to the Pacific Ocean, was much less cosmopolitan. In the central part of the north, mercenaries made a living. In the central part of the south, planters ran vast farms for corn, wood, beef, pork, and beginning in the 1690s, rice.
These Carolinians had joined the English planter colony on the Caribbean island of Barbados, which relied on African slave labor, and many of them themselves participated in the slave trade. For this reason, slavery played an important role in the development of the Carolina colony. (Split into North Carolina and South Carolina in 1729).
In 1732, inspired by the need to establish a buffer between South Carolina and the Spanish colonies in Florida, James Oglethorpe founded the English colony of Georgia. In many ways the development of Georgia anticipated the development of South Carolina.

In 1700 there were approximately 250,000 European colonists and Africans serving in the English colonies of North America. By 1775, on the eve of the revolution, there were about 2.5 million of them. The colonists did not have much in common, but they could unite and fight for freedom.
Tribal Nations Of The Thirteen Colonies
The American Revolutionary War (1775-1783) began after American colonists fought over issues such as taxation without representation in laws such as the Stamp Act and the Townshend Act. The growing tension came at the Battles of Lexington and Concord on April 19, 1775, when “the shot heard by all the world” was fired.
Nor was this without surprise; The Boston Massacre of March 5, 1770 and the Boston Tea Party of December 16, 1773 showed the growing discontent of the colonists with British rule in the colonies.
The Declaration of Independence, issued on July 4, 1776, listed the reasons why the Founding Fathers were forced by the authority of King George III and Parliament to disband the new nation. In September of that year, the Continental Congress proclaimed the United States of America as the United States.
France joined the war with the colonists in 1778, helping the British Continental Army defeat Britain at the Battle of York in 1781. The Treaty of Paris, which ended the American Revolution and granted independence to the original 13 colonies, was signed on September 3, 1783. .
Map Of The American Colonies: Population Density 1775
REAL CHECK: We are committed to accuracy and fairness. But if you see something that doesn’t look right, click here to contact us!
On May 14, 1607, a group of about 100 members was first founded in a joint venture called the Society of Virgins.
History of the 13 colonies, printable map of 13 colonies, blank map of 13 colonies, original map of 13 colonies, chart of the 13 colonies, old map of 13 colonies, colonial map of the 13 colonies, map of 13 colonies, map of the original 13 colonies labeled, the 13 english colonies map, geography of the 13 colonies, outline of the 13 colonies