Map Of Syria And Neighbouring Countries – Description: Detailed large political map of Syria with names of capitals, cities, states, provinces and borders with neighboring countries.
Syria is located in Western Asia and is officially known as the Syrian Arab Republic. The Mediterranean Sea and Lebanon lie in the west of the country, and Iraq in the east of the country. It has Jordan in the south and Turkey in the north. Damascus is the capital of Syria and the city is considered one of the oldest continuously inhabited cities in the world. Most people living in the country are Sunni Muslims, but there are also followers of other religions. More than four-fifths of the population of Syria are Arabs, and the rest are Turkmen, Kurds, Aramaic Syrians, Assyrians, Circassians and Armenians.
Map Of Syria And Neighbouring Countries

Syria has hot and dry summers and mild winters. The country is essentially a middle-income economy and is dependent on tourism, agriculture, industry and oil. Burjeslam is a very popular beach in the country. Agriculture is one of the most important sectors in Syria and employs more than 40% of the country’s workforce. About 1/4 of the country’s GDP comes from agriculture. Most of the people living in Syria are native to the Levant. The official language is Arabic. Although every effort has been made to follow the rules of citation style, some discrepancies may occur. If you have any questions, please refer to the appropriate style manual or other resources.
Syrian Violence Spills Into Lebanon And Turkey
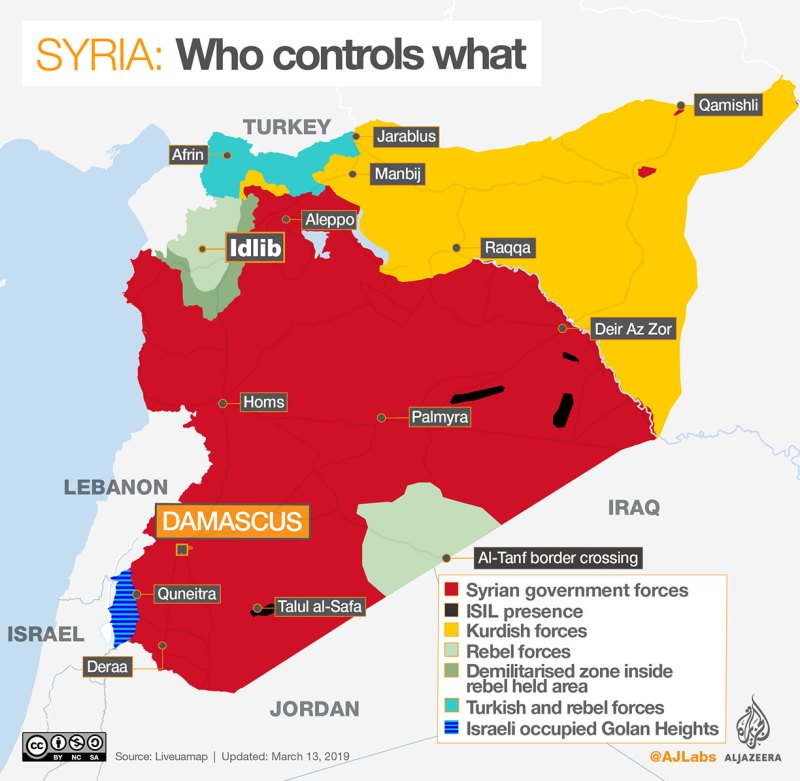
Syria, a country located on the eastern shore of the Mediterranean Sea in Southwest Asia. The area includes the area in the Golan Heights, which has been occupied by Israel since 1967. The current area does not correspond to ancient Syria, which was a strip of fertile land lying between the eastern coast of the Mediterranean Sea and the desert of northern Arabia. The capital is Damascus (Dimashq), on the Baradā River, located in an oasis at the foot of Mount Qāsiyūn.
After Syria’s independence in 1946, political life in the country was very unstable, largely due to strong friction between the country’s social, religious and political groups. In 1970, Syria came under the authoritarian rule of President Hafez al-Assad, whose main goals were to achieve national security and internal stability, and to recover Syrian territory that had been lost to Israel in 1967. Assad committed his country to a massive buildup of armaments, which severely strained the national budget, leaving little to develop. After Assad’s death in 2000, his son Bashar al-Assad became president. Despite some early steps toward political reform, Bashar al-Assad ultimately continued his father’s authoritarian style of governance, using the powerful Syrian military and security services to suppress political dissent. Long-suppressed internal tensions led to the outbreak of the Syrian Civil War in 2011.
Syria is bordered by Turkey to the north, Iraq to the east and southeast, Jordan to the south, and Lebanon and Israel to the southwest.
Syria has a relatively short coastline that stretches about 110 miles (180 km) along the Mediterranean Sea between the countries of Turkey and Lebanon. Sandy bays cut into the coast, alternating with rocky landings and low cliffs. North of Ṭarṭūs, a narrow strip of coast is cut off immediately to the east by the foothills of the northwestern Al-Anṣariyyah mountain range. It then expands into the ʿAkkār plain which continues south across the border with Lebanon.
Syria’s Kurds Face Squeeze After Regime, Turkey Meet In Moscow
The Al-Anṣariyyah mountain range borders the coastal plain and runs from north to south. The mountains are an average of 20 miles (32 km) wide, and their average elevation drops from 3,000 feet (900 meters) in the north to 2,000 feet in the south. Their highest point, with 1,562 meters, is east of Latakia. Immediately east of the mountains lies the Ghāb Depression, a 40-mile (64 km) long elongated trench that spans the valley of the Orontes River (Nahr Al-ʿĀṣī).
The Anti-Lebanon Mountains (Jabal Al-Sharqī) mark the border between Syria and Lebanon. The main ridge reaches a maximum height of 8,625 feet (2,629 meters) at Al-Nabk, while the average height is 6,000 to 7,000 feet (1,800 to 2,100 meters). Mount Hermon (Jabal Al-Shaykh), the highest point in Syria, reaches a height of 2,814 meters.
Smaller mountains are scattered across the country. These include the Al-Durūz mountain, which rises in the extreme south at a height of about 1,800 meters, and the Abū Rujmayn and Bishrī mountains, which lie northeast across the center of the country.

The rolling plains that occupy the rest of the country are known as the Syrian desert. Generally their height varies from 980 to 1,640 feet (300 to 500 meters); they are rarely less than 820 feet (250 meters) above sea level. The area is not a sandy desert, but includes rock and gravel steppe; the mountainous area in the south-central part of the country is known as Al-Ḥamād.
Syrian Arab Republic Map. Stock Vector. Illustration Of Abstract
The Euphrates River is the main source of water and the only navigable river in Syria. It originates in Turkey and flows southeast through the eastern part of Syria (
Tigris-Euphrates river system). The Euphrates Dam, built on the river at Ṭabaqah, was completed in the 1970s. The reservoir behind the dam, Lake Al-Asad, began to fill in 1973.
The Orontes is the most important river of the mountainous area. It rises in Lebanon, flows north through the mountains and the Ghab Depression, and enters the Mediterranean Sea near Antioch, Turkey. The Yarmūk River, a tributary of Jordan, drains the regions of Jabal Al-Durūz and Hawrān and forms part of the border with Jordan in the southwest.
Scattered lakes are found in Syria. The largest of these is Al-Jabbūl, a seasonal salt lake that permanently covers a minimal area of about 60 square miles (155 square kilometers) southeast of Aleppo. Other large salt lakes are Jayrūd northeast of Damascus and Khātūniyyah northeast of Al-Ḥasakah. Muzayrīb Lake, a small body of fresh water, is located northwest of Darʿā; the larger Qaṭṭīnahmar (Lake Homs), a body of water, lies west of Homs.
Syria Oil And Gas Overview, News And Maps
Most of the country’s sewage flows underground. At the surface, impermeable rocks – consisting of clay, marl (clay, sand or silt) and green sand – cover a relatively small area. Porous rocks cover about half of the country and consist mainly of sandstone or chalk. The very porous rocks consist of basalt and limestone. Water penetrates porous rocks to form underground springs, rivers or underground aquifers near the surface. Although springs are plentiful, aquifers are quickly depleted and can become saline in areas with low rainfall.
Due to the drought, vegetation plays a secondary role in the composition of the soil. With the exception of the black soil in the northeastern Al-Jazirah region, the soils are poor in phosphorus and organic matter. The most common soils are various loams and loams (mixtures of clay, sand and silt). Some are calcareous (lime); others, especially in the Euphrates valley area, contain gypsum. Alluvial soil is mainly found in the valleys of the Euphrates and its tributaries and in the Ghab depression.
The coast and the western mountains have a Mediterranean climate with a long dry season from May to October. In the extreme north-west there is light summer rain. On the coast, summers are hot with average daily highs in the low to mid 80s F (top 20s), while mild winters have average daily lows in the low 50s F (low 10s). Only above about 5,000 feet (1,500 meters) are summers relatively cool. Inland, the climate becomes dry, with colder winters and hotter summers. Maximum temperatures in Damascus and Aleppo average in the 90s F (mid 30s C) in the summer, while temperatures average low in the mid 30s to low 40s F (1 to 4 ° C) in the winter. In the desert, near Tadmur and Dayr al-Zawr, summer maximum temperatures average in the upper 90s to low 100s F (upper 30s to low 40s C), with extremes in the 110s F (mid to upper 40s C). Snow can come from the coast in winter and frost is common.

The coast and the western mountains receive 30 to 40 inches (760 to 1,000 mm) of precipitation per year. Annual rainfall falls sharply to the east: 10 to 20 inches (250 to 500 mm) falls in the steppes, more than 8 inches (200 mm) on Al-Durūz mountain, and less than 5 inches (130 mm) in the Al- Ḥamād desert area). ). The rainfall is variable from year to year, especially in spring and autumn. The civil uprising against Assad’s long rule turned into a protracted civil war. Here is a look at the elements that deepen the tragedy of Syria.
Political Map Of Jordan
Ten years since protesters in Syria first demonstrated against the Assad family’s four-decade rule, hundreds of thousands of Syrians have been killed and some twelve million people – more than half of the country’s pre-war population – have been displaced. . The country is plunged into an increasingly complex civil war: jihadists promoting a Sunni theocracy, overshadowed opposition forces fighting for a democratic and pluralistic Syria, and regional powers
Pakistan map and neighbouring countries, china neighbouring countries map, russia neighbouring countries map, syria and neighbouring countries map, neighbouring countries of syria, map of switzerland and neighbouring countries, india and neighbouring countries map, italy neighbouring countries map, syria neighbouring countries map, map of pakistan and neighbouring countries, map of china and its neighbouring countries, pakistan neighbouring countries map