Map Of Sumerian Civilization – The body of this article may be too short to adequately summarize the main points. Please consider expanding the prospectus to provide an accessible overview of all important aspects of the article. (October 2022)
The location of Jeral on a modern map and the main cities of Sumer along the ancient coast. In ancient times, the coastline extended almost to the Ura.
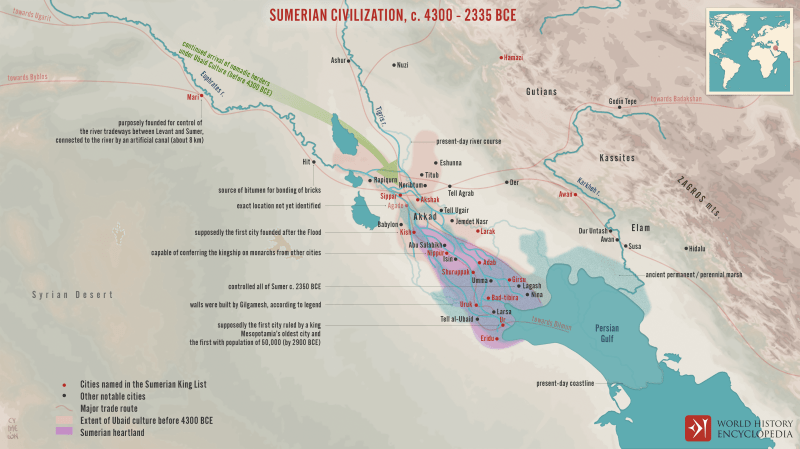
Map Of Sumerian Civilization
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/digital-illustration-of-the-fertile-crescent-of-mesopotamia-and-egypt-and-location-of-first-towns-112706582-5aa82360ba61770037a81f82.jpg?strip=all)
Sumer (/ˈsuːmər/) is the oldest civilization in the historical region of southern Mesopotamia (southern Iraq), emerging during the Chalcolithic and Early Bronze Ages between the sixth and fifth millennia BC. It is one of the cradles of world civilization along with ancient Egypt, Elam, the Carl Swope Civilization, Mesoamerica, the Indus Valley Civilization and ancient China. Living along the valleys of the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, Sumerian farmers grew many grains and other crops, which allowed them to build additional urban settlements. Proto-writing dates back to before 3000 BC. The earliest texts come from the cities of Uruk and Jamdeit Nasr and date from c. 3500 and c. 3000 BC
What Was The Fertile Crescent?
On the left: the bust of the Sumerian ruler Gudeya’s head, c. 2150 B.C. Right: Saĝ-gíg (𒊕 𒈪), cuneiform characters meaning “black-headed”, a local Sumerian sign. The first is a pictograph for “head” (, later), the second for “night” and “black” is pronounced gíg (, later).
The name given to the language spoken by the “Sumerians”, the ancient non-Semitic speaking inhabitants of southern Mesopotamia, their descendants the East Semitic speaking Akkadians.
The Sumerians called their land Kgir, ‘land of emperors’ (𒂗𒄀, k-gi(-r), lit. ‘country’ + ‘lords’ + ‘noble’), as well as in their inscriptions.
The origin of the Sumerians is unknown, but the Sumerians refer to themselves as “black-headed” or “black-headed”.
Geography Of Sumer.
[
For example, the Sumerian king Shulgi described himself as “the king of the four circles, the black-headed priest.”
The Akkadian word Šumer may represent a geographical name in the dialect, but the phonetic development leading to the Akkadian word šumerû is unclear.

Hebrew שִׁנְעָר Šinʿar, Egyptian Sngr, and Hittite shanhar(a) referring to southern Mesopotamia may be West Sumerian forms.
Map Of History Of Civilization Aleteia
Most historians have suggested that Schumer first settled permanently from c. 5500 and 4000 B.C. A West Asian people who spoke Sumerian (as evidenced by the names of cities, rivers, primary occupations, etc.), an isolated non-Semitic and non-Indo-European collective language.
Blau Monmouth combines proto-cuneiform characters and illustrations from the early Sumerian period of Jamdit Nasr, 3100-2700. g. B.C. British Museum.
Others have suggested that the Sumerians were a North African people who migrated from sub-Saharan Africa to the Middle East and were responsible for the spread of agriculture in the Middle East.
However, given the evidence that the first farmers descended from fertile crickets, this suggestion is often dismissed.
Mesopotamia The Emergence Of Civilization
Although not specifically referring to the Sumerians, Lazaridis et al. 2016 has suggested a partly North African origin for some pre-Semitic cultures of the Near East, especially after Gomez’s examination of Natufian, Natufian and Pre-Pottery Neolithic culture holders.
Alternatively, Ricketts’ (2013) genetic analysis of four ancient Mesopotamian skeletal DNA samples suggests a Sumerian connection to the Indus Valley Civilization, possibly as a result of ancient Indus-Mesopotamian links.
According to some data, the Sumerians are related to the Hurrians and Urartians, and the Caucasus is considered their homeland.

The prehistoric people who lived in this region before the Sumerians are called “Proteifrat” or “Ubedites”.
Early Civilizations In Mesopotamia
The Ubaids, although never mentioned by the Sumerians themselves, are considered by modern scholars to be the first civilizing force of the Sumerians. They drained swamps for agriculture, developed trade, and established industries including weaving, leatherwork, metalworking, masonry, and pottery.
Some scholars dispute the idea of a Proto-Ephratean language or sublanguage. They believe that the Sumerian language may have originally belonged to a hunting and fishing people who lived in the marshes and coastal region of eastern Arabia and were part of the dual culture of Arabia.
Reliable historical records begin much later. There is no type in Sumara that dates earlier than Mebargesi (Early Dynasty I). Joris Zarin believes that the Sumerians lived along the coast of eastern Arabia in what is now the Persian Gulf before the Ice Age flood.
The Sumerian civilization developed during the Uruk period (4th millennium BCE), which continued into the Jamdeat Nasr and Agra dynasties.
Map Of Sumeria C3000 Bce By Adam Mckithern
The Sumerians gradually lost control over the Semitic states from the northwest. Sumer was conquered around 2270 BC by the Semitic-speaking kings of the Akkadian Empire (a brief history), but the Sumerian language continued as a sacred language. Local Sumerian power re-emerged for about a century during the Third Dynasty of Ur, around 2100-2000. g. BCE, but Akkadian also remained in use for a time.
The Sumerian city of Eridu, located on the Persian Gulf coast, is considered one of the oldest cities in which three distinct cultures coexisted: the Ubidean farmers, who lived in mud-brick huts and engaged in irrigation; mobile nomadic Sami priests who live in black tts and follow herds of sheep and goats. and Fishermen living in reed huts in the swamps, who may be Sumerian ancestors.
At the end of the 4th century BC, Sumer was divided into several independent city-states separated by canals and boundary stones. Each was built on a temple dedicated to the city’s particular patron god or goddess and ruled by a priestly governor (c) or king (logal) closely associated with the city’s religious practices.

Ziggurat of Anu and the White Temple in Urka. The original pyramidal structure “Ano Ziggurat” dates to around 4000 BC and the White Temple was built on top of it. 3500 BC
File:cities Of Sumer (en).svg
The design of the ziggurat was probably the forerunner of the Egyptian pyramids, which date back to the 1st century BC. 2600 BC
With the exception of Mari, a full 330 km (205 mi) northwest of Agada, but known as “royal use” in the early King List of Dynasty II, and Nagaru, an outpost, these are all cities. In the Euphrates-Tigris plain, south of Baghdad, in the present-day Iraqi governorates of Babil, Diyala, Wasita, Dikar, Basra, Manassas, and Al-Qudsiyya.
The hairstyle of the captives (curly on top and short on the sides) is characteristic of the Sumerians, as is the standard of Ur.
The Sumerian city-states came to power in the prehistoric Ubaid and Uruk periods. Sumerian written history dates back to the 27th century BC and earlier, but historical records are unclear until the Early III Dynasty period. 23rd century BC, which developed the now understood cursive writing system that allowed archaeologists to read contemporary records and inscriptions. The Akkadian Empire was the first state to successfully unite large parts of Mesopotamia in the 23rd century BC. After the Gutian period, the Ur III empire similarly united northern and southern Mesopotamia. It was invaded by the Amorites at the beginning of the second millennium BC. The “House of Blood” of the Amorites existed until the year 1000. 1700 BCE Mesopotamia was united under Babylonian rule.
The Civilization Of Sumer
The Ubaid period is characterized by a remarkable style of painted pottery that flourished in Mesopotamia and the Persian Gulf. The oldest evidence of occupation comes from Tell el-Oili, but given that the forest conditions of southern Mesopotamia were favorable for human occupation before the Ubid period, it is possible that older sites existed but have not yet been found. This culture appears to have been derived from the Sumerian culture in northern Mesopotamia. It is not known whether they were the true Sumerians identified with the later Urian culture. The story of the transfer of the gifts of civilization to Inana, goddess of Uruk and goddess of love and war, may reflect the transition from Ki, god of wisdom and chief deity of the Aredu, from Eridu to Uruk.
The archaeological transition from the Ubid period to the Uruk period is marked by a shift from painted pottery produced locally on a slow wheel to unpainted pottery produced by specialists on a faster wheel. A gradual transition to a larger type. The Yurok period is a continuation and extension of the Ubaid period with significant changes in pottery.
By the Uruk period (ca. 4100-2900 BC), the volume of goods transported along the canals and rivers of southern Mesopotamia led to many large, flat, temple-built cities (populations of over 10). Contributed to the increase , 000 people), where specialized employees worked in the centralized administration. It is fairly certain that it was during the Eureka period that Sumerian cities began to use the labor of slaves captured from the highlands, and there is much evidence of captured slaves as laborers in early texts. samples and ev colonies

Sumerian ancient civilization, the sumerian civilization, timeline of sumerian civilization, images of sumerian civilization, sumerian civilization, contributions of sumerian civilization, characteristics of sumerian civilization, fall of sumerian civilization, sumerian cradle of civilization, history of sumerian civilization, location of sumerian civilization, features of sumerian civilization