Map Of Ancient Middle East With Cities – Any attempt to follow the rules of citation style may result in inconsistencies. If you have questions, consult the appropriate style manual or other resources.
Join the Publishing Partner Program and our community of experts to get a global audience for your work.
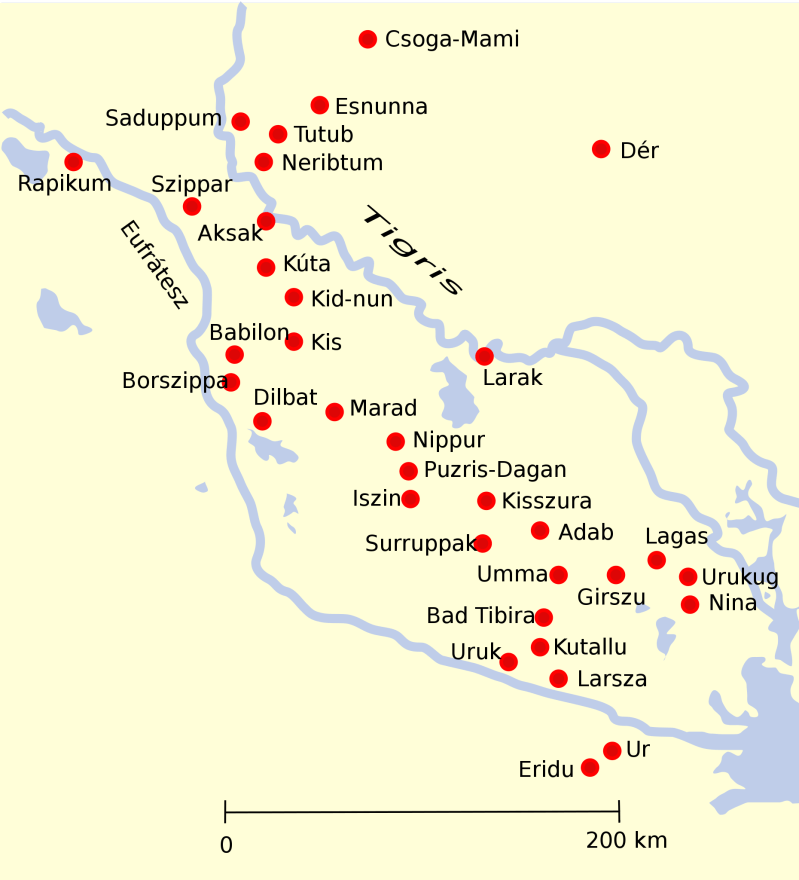
Map Of Ancient Middle East With Cities

Ancient Middle East Prehistoric Mesopotamia; Local history up to the rise of civilization in Egypt and elsewhere.
Middle East Map With Cities And Islands For Free Used
The height of civilization in the Middle East is summer or winter; This is mainly due to the presence of land and road bridges which make it easy to travel during dry or wet seasons. North of the Caspian Sea, many people find it almost impossible to migrate in winter. Central Eurasia is often very dry due to extreme weather during the summer. The land route between Asia and Africa was initially limited to a narrow strip of land in the Suez Islands. Major desert travel is limited to special routes east and west of the Nile Valley in Iran and North Africa.
Another reason for the region’s early importance in world history is that the water supply and climate were ideal for starting agriculture. Many species of rice grow wild and tributaries are easily drained or irrigated for wild wheat and barley seed. Under normal conditions, seeds should be spread over a sufficiently moist surface to ensure a single crop. It is not surprising, therefore, that simple agriculture is evidenced in the 8th or 9th millennium BC, when more excavations were carried out at earlier sites than elsewhere in Palestine, particularly in the Middle East. A number of bone sickles and flint sickle tips have been found at Palestinian sites between 9000 and 7000 BC.
In Mesopotamia and Iran, remains of this period are found in caves in the lower Zagros Mountains of western Iran and western Iraq. The date of the beginning of a large-scale irrigation system in Mesopotamia is doubtful, since most of the early sites of the irrigated culture were covered by alluvium from the spring floods of the Tigris and Euphrates rivers. Archaeologists once thought that all irrigation originated in the foothills of the Zagros, and that the earliest true farmers lived in the plains of Iran. But recent excavations and surface excavations have shown that irrigation of the Tigris and upper Euphrates, as well as their tributaries, began in the 6th millennium BC (eg, al-Qawm on the upper Euphrates). By the 7th millennium BC, small-scale irrigation was prevalent in Palestine (eg, Jericho).
History Quiz: Fact or Fiction? Immerse yourself in history as this puzzle unravels the past. Find out who actually invented the moving type known as the “Mum” Winston Churchill and when he first heard the sonic boom.
Ancient Near East: Cradle Of Civilization
During moderate river flooding in northern and eastern Mesopotamia, the rivers were partially diverted during the flood, flowed more or less parallel to the rivers, and could have been used to irrigate a wide area. This type of diversion dam irrigation avoids the disadvantages of large storage dams; In particular, the risk of dumping large amounts of waste into the storage basin behind the dam was avoided. To the north and east, while southern Mesopotamia was mostly marshland like the early Egyptian delta, many cities were established, developing in places like Nineveh only after the 5th millennium BCE. The flow of the Euphrates River is much lower than that of the nearby Tigris. The latter is faster because it is more difficult to control, but more important for irrigation.
The Egyptian Nile has a more predictable watercourse than the rivers of Mesopotamia because it avoids the occasional Mesopotamian floods and is plagued by unusually high annual floods.
The world’s oldest urban and literate civilization was developed in Mesopotamia by the Sumerians in the late 4th millennium BC. Around 2300 BC, Sargon I, a Semitic-speaking leader, conquered all the Babylonian kingdoms and founded the first Akkad (Akkadu), which ruled for a century and a half. Sargon and his successors first gained control of the Crescent and adjacent regions of Southwest Asia. They sent trade expeditions as far as central Anatolia and Iran, as well as India and Egypt. After the fall of the Akkadian dynasty, there was a Sumerian revival under the Third Dynasty of Ur (Ur III [21st-20th century]), followed by further arrivals of Semitic-speaking peoples. These people founded the First Dynasty of Babylon (19th to 16th centuries), the most important king being Hammurabi. In the 17th century, new ethnic groups appeared in both Babylonia and Syria-Palestine: Kassites from the Zagros Mountains; Present day Hurrians from Armenia and Indo-Europeans from Central Asia. This period marks the end of the formative phase of Mesopotamian civilization.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-469298084-596ad2533df78c57f4a72d88.jpg?strip=all)
Shortly after 3000 BC, the small states that arose in the Nile Valley were united under the 1st Dynasty of Egypt. By that time, the Egyptians had already developed a writing system. Between about 2686 and 2160 BC, their country was united under a powerful monarchy (Kingdom) served by a complex bureaucracy (Old Kingdom).
File:ancient Egypt And Mesopotamia C. 1450 Bc.png
There was a period of unification in the late 3rd millennium and a reunification under the 12th Dynasty (1991–1786).
During these two centuries he controlled Egypt, Nubia, Libya, Palestine and southern Syria. After 1800 BC, the Egyptian Empire disintegrated and around 1700 Egypt was occupied by the Asian “Hykkas”, who ruled Egypt for a century and a half.
A local 18th dynasty flourished in Egypt before the end of the 16th century BC. He expelled the Hyksos and established a new kingdom. The rulers of the new kingdom returned to Syria-Palestine and clashed with the Mitanni-Harian kingdom and later with the Anatolian Hittites, who spread from the north into Syria in the 14th century BC. The Amarna Letters (diplomatic letters written in the Babylonian alphabet and language and discovered in Egypt by archaeologists) are an important source of information about this period. The dominant powers in Mesopotamia were Kassite Babylonia and Assyria (derived from Mitanni subjugation in the early 14th century BC). Relations between states were governed by elaborate treaties and were constantly broken up. After the fall of Mitanni (ca. 1350), both the Hittites and the Babylonians became hostile to Assyria. Kassite Babylonia fell to Assyria around 1230. This was followed by the fall of the Hittite Empire (ca. 1200), which has been called the first “International Age” of the civilized world.
Late 13th century BC, Aegean region; Anatolia and the Fertile Crescent saw the new people degenerate. Their face was the Trojan War; The Hittite Empire and the Fall of Greece; This coincided with the destruction of many coastal cities in Cyprus and Syria-Palestine. Most prominent among the settlers from the west were the Phrygians, who occupied much of the old Hittite heartland, and the Philistines who moved into Palestine.
Large Detailed Relief And Political Map Of Middle East With All Capitals And Major Cities
At the same time, in Transjordan and western Palestine, the Hebrews established the Hebrew tribe that developed into the kingdoms of Saul and David.
Earlier, Iranian tribes led by the Medes entered Iran from Turkistan. The Syrians came from the south and west. The Arameans and Medes changed the ancient Middle East.
In the 11th century BC, the Assyrian kingdom suffered an eclipse and Arameans and related tribes conquered much of its territory. The Assyrians did not recover until the late 10th century, but by 850 they had conquered western Media and southern Armenia, as well as Babylonia and Syria. In the following centuries, the empire expanded greatly until 630. The administration was also highly organized. Its language became Aramaic.

The Canaanite Phoenicians re-established their trading community on the Syrian coast after the invasions of the Philistines and Arameans. In the 10th and 9th centuries, they migrated to the Mediterranean and established Spanish colonies in North Africa and the Far West. Their influence in the western Mediterranean declined after the 6th century. Their Carthaginian colonies then took over Phoenician trade in the western and central Mediterranean.
Map Of Egypt
Further east, the Medes and Chaldeans destroyed the Assyrian Empire in the late 7th century. The Chaldean dynasty of Babylon adopted Assyrian administrative traditions and encouraged trade. Under Nebuchadrezzar II (c. 605–c. 561 bce), their Neo-Babylonian empire became the most powerful political entity of its time. His rule extended from the Taurus Mountains in Anatolia to eastern Arabia and southern Iran. This transitory state is huge.
Map of ancient middle east countries, middle east cities map quiz, ancient middle east map, ancient biblical map of the middle east, map of middle east cities, map of middle east with capital cities, map of ancient middle east civilizations, ancient middle east cities, map of ancient middle east and egypt, map of ancient middle east, blank map of ancient middle east, map of middle east countries and cities