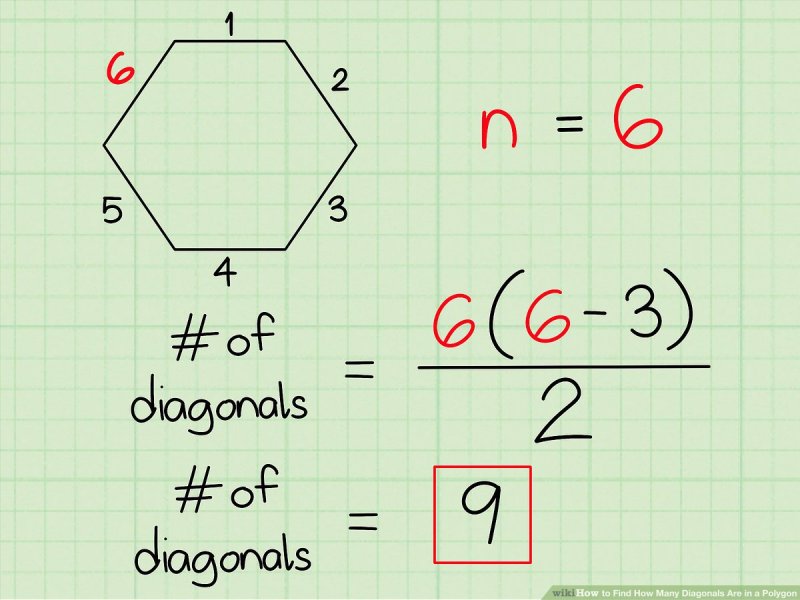
How Many Diagonals Does A Parallelogram Have – In Euclidean geometry, a parallelogram is a regular (non-self-intersecting) rectangle with two pairs of parallel sides. Opposite or opposite sides of a parallelogram are of equal length and opposite angles are of equal measure. The union of opposite sides and opposite angles is a direct consequence of Euclid’s parallel postulate, and no condition can be proved without reference to Euclid’s parallel postulate or one of its equivalent formulas.
By comparison, a quadrilateral with only one pair of parallel sides is a trapezium in American Glish, or a trapezium in English.
How Many Diagonals Does A Parallelogram Have

A regular (non-self-intersecting) quadrilateral is a parallelogram if one of the following statements is true:
Properties Of Parallelogram, Rhombus, Rectangle And Square: Examples
Thus, all parallelograms have all the properties listed above, and conversely, if only one of these statements is true for a regular rectangle, then it is a parallelogram.
All area formulas for general convex quadrilaterals apply to parallelograms. The following formulas are typical for parallelograms:
A parallelogram with base b and height h can be divided into a trapezoid and a right triangle and made into a rectangle as shown in the figure to the left. This means that the area of a parallelogram is the same as a rectangle with the same base and height:
The area of a parallelogram is the area of the blue region that is the interior of the parallelogram
If The Diagonals Of A Parallelogram Are Equal, Then Show That It Is A Rectangle
The base × height area formula can also be derived using the figure on the right. The area K (blue area) of a right parallelogram is less than the total area of the rectangle and the area of the two orange triangles. the area of the rectangle
K = K rect – 2 × K tri = ( ( B + A ) × H ) – ( A × H ) = B × H . }-2times K_}=((B+A)times H)-(Atimes H)=Btimes H.}
The area of the parallelogram containing the sides B and C (B ≠ C) and the angle g at the intersection of the diagonal is expressed as follows.

Here, the parallelogram is determined by the lengths B and C of the two adjacent sides.
Solved] Hi, I Need Help On My Homework, Thanks For Taking The Time To…
Here S = ( B + C + D 1 ) / 2 )/2} and the leading factor 2 comes from the chous diagonal dividing the parallelogram into two congruent triangles.
K = | det [ a 1 a 2 1 b 1 b 2 1 c 1 c 2 1] | . a_&a_&1\b_&b_&1\c_&c_&1d}right|.}
Also, since the opposite sides of a parallelogram are lg, side AB is equal to DC.
Diagonals AC and BD bisect each other into segments of equal length, so the diagonals bisect each other.
Diagonals Parallelogram Math Stock Vector (royalty Free) 1950064459
Separately, diagonals AC and BD bisect each other at point E, point E being the midpoint of each diagonal.
Parallelograms can be tiled by translating the plane. If the edges are equal or the corners are right, the symmetry of the lattice is high. This shows the four Bravai lattices in 2 dimensions.
Equilateral triangle – the median is equal to the sides (albeit in a different order). If ABC is an equilateral triangle with opposite side a, G is a ctroid (where the three medians of ABC intersect) and AL is one of the extended midpoints of ABC, and if L lies on the circumference of ABC, then θ BGCL parallelogram.

The midpoints of the sides of an arbitrary quadrilateral are the vertices of a parallelogram, called its Verignon parallelogram. If the quadrilateral is convex or concave (that is, does not intersect itself), then the area of the verignon parallelogram is half the quadrilateral.
Question Video: Calculating A Rhombus’s Diagonal Length Given Its Area
Two diameters for an ellipse are said to be conjugate if the tangent line of the ellipse at a point on one diameter is parallel to the other diameter. Each pair of elliptic diameters has a corresponding tangut parallelogram, sometimes called a bounding parallelogram, formed by the tangut lines of the ellipse at the four points of the conjugate diameter. All tangut parallelograms for a given ellipse have the same area.
An ellipse can be reconstructed from any pair of conjugate diameters or from any tangent parallelogram.ematic stack exchange. A question and answer site for students of any level and professionals in related fields. It takes a minute to register.
The diagonals of the parallelogram are $8$ and $4$. They meet at $60°$. Find the sides and area of the parallelogram.
I’ve tried using the cosine rule here with 4 and 2 as sides and 60° as angle. But the answer I got is different from the answer key. Also, what about the pitch and the other two sides?
Area Of Parallelogram
You can calculate the area directly by looking at the intersection of the diagonals, as shown in the figure above.
Then note that the opposite triangles are also congruent by ASA. The angle of one pair of triangles is 60º, and the angle of the other is 120º. Thus, the area of the parallelogram is $2 cdot frac(4)(2) sin 60º + 2 cdot frac (4)(2) sin 120º = 8sqrt$.
You must be logged in to answer this question. Not the answer you’re looking for? Check out other trigonometry questions called area of a triangle rectangle.

By clicking Accept All Cookies, you agree that StackExchange may store cookies on your device and disclose information in accordance with our cookie policy. Every geometry class or course includes an in-depth study of the properties of parallelograms. In this post, we’ll quickly review the basic properties of parallelograms, including sides, angles, and congruent relationships.
Parallelogram With Diagonals
Finally, we determine whether the parallelogram has line symmetry or not. And if the parallelogram has linear symmetry, what would the parallel lines of symmetry look like (diagrammatically).
Before answering these basic questions about the symmetry of parallelograms, let’s quickly review the properties of parallelograms:
Definition: A parallelogram is a special type of quadrilateral (a closed quadrilateral) in which opposite sides are parallel and of equal length.
Also, opposite interior angles in any parallelogram have equal value. And any pair of adjacent interior angles in a parallelogram is supplementary (their sum is 180 degrees).
Solved] In Parallelogram Math, Diagonals Mt And Ah Intersect At E. If At…
Now that you understand the basic properties of parallelograms and angle relationships, you’re ready to explore the following questions:
For starters, a line of symmetry is an axis or imaginary line that can pass through the center of a shape (facing in any direction) to divide the shape into two equal parts that are mirror images of each other. let’s emphasize.
For example, a square, rectangle, and rhombus all have line symmetry because at least one imaginary line can be drawn through the center of the shape that cuts it into two equal parts that are mirror images of each other.

In fact, a shape can have several lines of symmetry. In the diagram below, you can see that a square has four lines of symmetry, while a rectangle and a rhombus only have two lines of symmetry.
Area Of Parallelogram Whose Diagonal Vectors Are Given
But why parallelograms do not have lines of symmetry? Because, for any parallelogram, it is impossible to construct a line of symmetry (an axis or imaginary line that passes through the center of the figure and divides the image in half, where each side is a mirror image of the other).
You can go ahead and try to draw a line of symmetry in any parallelogram and you will find that it is impossible.
In geometry, rotational symmetry means that a shape or figure is the same as its predecessor and is rotated by several degrees.
A parallelogram has rotational symmetry because the original or previous image has the same number after being rotated 180 degrees.
How Many Diagonals Does Atriangle Have
In today’s lesson, we studied parallel lines of symmetry, whether they exist or not, whether parallelograms have symmetry.
Having considered the properties of a parallelogram, namely that it is a rectangle with equal sides and opposite angles, we moved on to determine whether a parallelogram has any line symmetry.
Applying the definition of a line of symmetry, we conclude that while shapes such as squares and rectangles do indeed have lines of symmetry, parallelograms do not.

A parallelogram has zero lines of symmetry because it is impossible to draw a line through the center of any parallelogram that divides the figure into two equal parts that are mirror images of each other.
Solved: ‘can You Conclude That This Parallelogram Is A Rectangle? Explain. Hn Simmo; Objectives Quiz: Special Parallelograms 7 Quadrilaterals Can You Conclude That This Parallelogram Is A Rectangle? Explain. Ing 100 Es
Although parallelograms do not have linear symmetry, they do have rotational symmetry because any parallelogram rotated 180 degrees results in the figure you started with. Ematics Stack Exchange is a community question and answer site. Professionals of any level of education and related fields. It takes a minute to register.
I had the idea of arranging four similar right triangles in such a way that the right angles are adjacent. For example
Does a parallelogram have perpendicular diagonals, how to solve a parallelogram with diagonals, parallelogram properties diagonals, parallelogram diagonals formula, how to find diagonals of a parallelogram, parallelogram diagonals perpendicular, diagonals parallelogram, parallelogram area formula diagonals, how many diagonals does a parallelogram have, parallelogram diagonals bisect angles, area of parallelogram diagonals, parallelogram with perpendicular diagonals