3d Cube Faces Edges Vertices – When we look around us, we notice that all objects have a shape. Everything from a computer to a book has a unique design. Shapes are two-dimensional or three-dimensional. A shape that has length and width is called a two-dimensional shape (also called a 2-D shape), and a shape that has length, width, and height is called a three-dimensional shape (also called a 3-dimensional shape mentioned). D shape). D shape).
A solid shape is a 3-D shape that has 3 dimensions, which are length, width and height (depth). In this article we will learn about solid shapes and how to visualize them.
3d Cube Faces Edges Vertices

2-D shapes are flat geometric figures composed of straight or curved lines. They only have length and breadth (width). 2-D shapes have no depth. Circles, triangles, squares and rectangles are some examples of two-dimensional shapes. Shapes that consist of three or more straight lines are called ‘polygons’. Some common two-dimensional shapes are circle, oval, triangle, square, diamond, rhombus, parallelogram, rectangle.
D Shapes: List Of All Kinds Of 3d Shapes In English • 7esl
A 3-D shape or solid shape has length, width and height. The complete form takes up some space and rests on one or more surfaces. Cubes, cones, spheres, cubes are some examples of solid shapes. Many objects in the real world, such as a book, a laptop, a ball, a birthday cone, look like solid shapes. Some three-dimensional shapes are cuboid, sphere, cone, cylinder, pyramid, cube.
All solid shapes are defined by a certain number of faces, vertices and edges. Let’s understand each of these terms.
Each individual surface of a solid shape is called a face. For example, a cube has 6 faces. Look at the figure below, which shows the face of a cuboid.
In fixed form, a ‘Vertex’ is defined as the point where two or more lines meet. Vertices is the plural form of ‘Vertex’. A sphere is an unusual shape that has no top. Take a look at the following image which shows the top of the cube.
Set Of Abstract 3d Geometric Shapes From Triangular Faces For Graphic Design. Frames Volumetric Gold Form With Edges And Vertices. Geometry Scientific Concept Isolated On White Background. Stock Vector
In solid form, an ‘Edge’ is defined as a line segment that connects two points or two corners. The following image shows the edge of a cube.
All solid shapes have top, side and front views. Let’s check each of them.
Imagine cutting a solid shape horizontally or vertically. We can clearly see that it looks like a two-dimensional shape (like a square or rectangle). This is called a “cross section”. The shape we get depends on the solid shape we cut. For example, see the image below, in which a cylinder is cut horizontally and vertically. The horizontal section looks like a rectangle, and the vertical section looks like a circle.

Imagine that the light source falls on a solid shape, say a cone. A solid shadow forms a 2-D shape. In the image below we see that when the light source falls on the thin end (top) of the cone, we get a shadow as a 2-D shape, which is a circle.
Geometry Nets Information Page
Consider a Rubik’s cube (a real example of a solid shape – a cube) that has 27 small cubes inside. Each cube has 1 unit. This means that if we stack 3 rows of 3 cubes, we get a cube that has 27 small cubes, each with 1 unit.
The solid shape grid represents its unfolded shape. In other words, if the surface of a three-dimensional shape is unfolded and laid down, any face can be perceived as a two-dimensional shape. This pattern we get is called a grid. For example, a cylinder mesh is shown below. We can clearly see that there are two 2-D shapes in it. One is a circle and the other is a rectangle.
We can represent a 3-D shape in a 2-D flat surface such as paper. We can do this in two ways.
Isometric sketches are drawn on isometric dot paper with exact measurements. The figure below shows an isometric sketch of a cube on isometric dot paper.
D Shapes, Faces, Edges And Vertices
Solid shapes are three-dimensional shapes that have length, width and height (depth). Cubes, cones, spheres, cubes are some examples of solid shapes.
A flat surface of a solid shape is called a face. A line segment that connects two faces of a solid shape is called an edge. The point or the corners where two edges meet is called a vertex.
No, 2-D shapes only have vertices. For example, a triangle has 3 vertices and a square has 4 vertices.

Yes, solid shapes can be drawn on flat surfaces using the oblique sketching technique or the isometric sketching technique. A two-dimensional shape has length and width. A three-dimensional solid form also has depth. Three-dimensional shapes, by their nature, have an interior and an exterior, separated by a surface. All physical objects, things you can touch, are three-dimensional.
D Shapes (year 2)
This page covers both straight-sided solids called polyhedra, which are based on polygons, and solids with curves, such as spheres, cylinders, and cones.
Polyhedra (or polyhedrons) are solid shapes with straight sides. Polyhedra are based on polygons, two-dimensional plane shapes with straight lines.
Polyhedra are also often defined by the number of edges, faces, and vertices they have, as well as whether all their faces are the same shape and size. Like polygons, polyhedra can be regular (based on regular polygons) or irregular (based on irregular polygons). Polyhedra can also be concave or convex.
One of the most basic and well-known polyhedra is the cube. A cube is a regular polyhedron that has six square faces, 12 edges and eight vertices.
Faces And Vertices Of 3d Shapes (year 2)
The five regular solids are a special class of polyhedra whose faces are all equal, each face being a regular polygon. Platonic solids are:
A prism is any polyhedron that has two congruent ends and straight sides. If you cut a prism anywhere along its length, parallel to the end, its cross section is the same – you would end up with two prisms. The sides of the prism are parallelograms – four-sided shapes with two pairs of sides of equal length.
Antiprisms are similar to regular prisms in that their ends match. However, the sides of an antiprism are made of triangles, not parallelograms. Antiprisms can be very complex.

Although we think of pyramids with a square base, like those built by the ancient Egyptians, they can actually have any polygonal base, regular or irregular. Additionally, a pyramid can have its top in the direct center of its base, i.e. a right pyramid, or it can have its top off-center if it is an oblique pyramid.
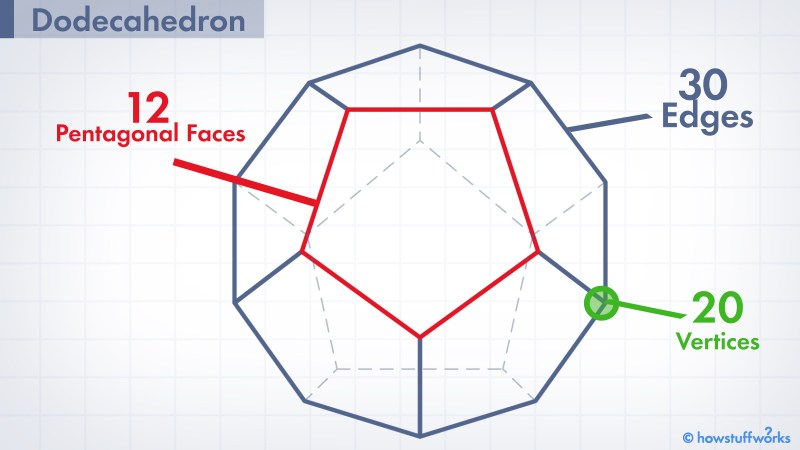
Dodecahedron: The 12 Sided Shape With The 12 Letter Name
A truncated cube (as shown) is an Archimedean solid with 14 faces. Six faces are regular octagons, and the other eight are regular (equilateral) triangles. A shape has 36 edges and 24 vertices (corners).
Solid shapes that include a curved or rounded edge are not polyhedra. Polyhedra can only have straight sides. Also see our page on 2D Curved Shapes.
Many objects around you will include at least some curves. In geometry, the most common curved bodies are cylinders, cones, spheres and tori (plural for torus).
The cylinder has the same cross-section from one end to the other. Cylinders have two equal ends of a circle or oval. Although similar, cylinders are not prisms because a prism (by definition) has a parallelogram, straight sides.
Drawing Geometric Shapes
A cone has a round or oval base and a top (or top). The side of the cone tapers smoothly to the top. A cone is similar to a pyramid, but differs in that the cone has a single curved side and a round base.
In the shape of a sphere or globe, a sphere is a perfectly round object. Every point on the surface of the sphere is equidistant from the center of the sphere.
In the form of a ring, tire or donut, a regular ring torus is formed by turning a smaller circle around a larger circle. There are also more complex forms of tori.
Our area calculation page explains how to calculate the area of two-dimensional shapes, and you need to understand these basics to calculate the area of three-dimensional shapes.
Topic: Geometric Reasoning E1.1
You can use your knowledge about the area of two-dimensional shapes to calculate the area of a three-dimensional shape, because each face or side is actually a two-dimensional shape.
And so on. You can read more about units of measurement on our measurement systems page.
The area of a cube is the area of one face (length x width) multiplied by 6, because all six faces are equal.
Since the face of the cube is a square, you only need to make one measurement – the length and width of the square are by definition the same.
D Shapes (face, Edge, Vertice) Worksheet
. We multiply by 6, the number of faces on the cube, and we find that the surface of this cube is 600 cm
Similarly, the area of other regular polyhedra (platonic solids) can be calculated by finding the area of one side and then multiplying the answer by the total number of sides – see
3d shapes rectangular prism faces edges vertices, 3d shapes properties faces edges vertices, 3d shapes cube faces edges vertices, 3d shapes edges vertices and faces chart, 3d shapes cone faces edges vertices, cube faces edges vertices, 3d shapes faces edges vertices, 3d shapes cylinder faces edges vertices, 3d shapes pyramid faces edges vertices, 2d and 3d shapes faces edges vertices, faces vertices and edges, 3d faces edges vertices
