Bike Gears Explained – Understanding bike dimensions is often taught early in life to new cyclists. Gearing plays an important role in competition and training. The goal of every cyclist is to try to choose the best gear for their physiology and abilities in order to overcome different types of races.
Too big a tool and you’ll have a hard time getting to the top, too small and you’ll spin in the endgame or struggle to get more.
Bike Gears Explained

In endurance events, it’s important to find equipment that allows you to keep racing and run faster (for example, in competitions). For short events such as 200m running or flying, choose equipment that can produce the maximum power output in watts compared. 200m run is important. From designing your bike setup (wheel circumference, etc.) to using a wide range of tools and using your power is the first step to getting basic performance.
Complete Guide To 6 Speed Bike Gears
Different tools help you develop different parts of your physiology. For example, larger equipment can help improve strength, and smaller equipment can improve muscle coordination and speed.
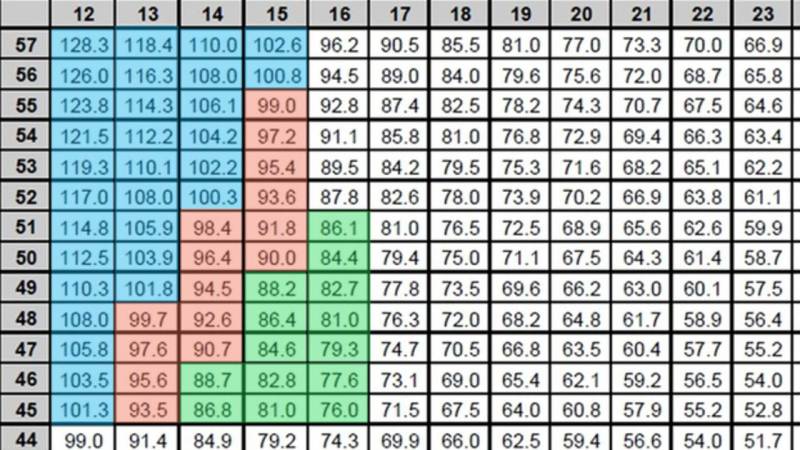
The equipment chart below is an example used by Omnium his riders who participate in various events and complete various training activities.
You will find riders covering equipment diagrams to easily identify different pieces of equipment used in different training activities and types.
* It is important to note that equipment is individual. The colored equipment table below shows the so-called ‘small’, ‘medium’ and ‘large’ equipment for a particular player in the field.
Gear Big Cycle Clearance, 56% Off
The “small” tools are painted green and are spaced between 76 and 88 inches. The important thing to keep in mind is that riders choose different tools from the green section to complete different types of power for different competitions.
The group of large equipment (blue shaded area) he is 100-128 cm and if the rider is unable to use all connected equipment from that area use various combinations, as in the previous example. to complete the various forms. power and performance.
A 100-centimeter machine can be used to reach a certain distance between workers in training and focus on the average wattage for a certain period of time. A 115-centimeter device can be used to complete the acceleration of the seat and increase the power of the bike.

When it comes to running gear selection, it’s important to choose gear that can provide a good and sustained cadence for the duration of the event. You should also consider the equipment that can produce the maximum wattage at the required height. In some cases, you can use these tools to attack, do well in sprints, and gain the power to repeat the process (for example, point races).
How To Use Bike Gears
Here are some basic tips for considering the best options.
1. Run a maximum cadence test and find out your cadence. This gives you the basics and things you can refer to to analyze your progress, especially in practice.
2. Analyze your event/discipline to create the energy system you use the most and what you can achieve based on your average cadence throughout the event.
3. For shorter sprint type events, use several trials at different bike speeds to build up your power output and taper off over 30 seconds.
Bike Gears Explained
4. If you have inherited previous equipment, analyze your bike equipment to find out what works for you in terms of a) efficiency over time and b) power output over time. please give me.
5. Try to improve your strength, power and speed by completing exercises on your bike. Above all, though, make sure this exercise is specific to what you do on your bike. This allows you to transfer these qualities with your pedal stick to generate more power, faster and at the same time with better technique!
6. Evaluate your strengths and weaknesses as an athlete and consult with us or your coach who has the ability to provide a training facility and competitive environment with the overall goal of helping you improve and progress in your chosen category. please.

I’ll help you! We’ve put together a plan to help you find ways to reach your 2021 cycling goals. Gear is one of the most frustrating parts of cycling for many people. It’s not just you. We’ll talk about 7 gears, what they look like on your bike, how to use them, and when they work best (and when they don’t).
Bike Gears Explained
If you sit on a 7-speed bike and look down at the right pedal, you’ll see something like the image below.
The right pedal grips the crank arm, which is connected to the “chainring”. A gear that rotates when you step on the pedal. It is the chain that runs on the chain. The role of the chain is to transmit the power of the pedals to the rear wheels.
As you follow the chain back to the rear wheel, the chain passes over the toothed cog (known as the “rear cassette”, seven speed bikes have seven cogwheels) and below it is the area with the two smaller cogwheels. (this is known as a “rear cassette” derailleur).
7-speed broadband access is available. Most of them will be what are commonly known as “hybrid vehicles”. This bike can be used in a variety of situations, from walking on the beach, running in the park with the family, to commuting to work. Hybrid bikes are also called city bikes, commuter bikes, fitness bikes and cross-country bikes.
A Guide To Bicycle Gears: How To Shift Bike Gears And Do It Smoothly
There are also seven of his accessories for other types of bikes, such as e-bikes and beach bikes.
This equipment provides plenty of support when going around rolling hills. A 7-speed bike is usually sufficient for such hills. However, if you regularly ride steep terrain, it’s worth considering a mountain bike instead.
Similarly, on flat roads and trails, 7-speed allows you to move at a comfortable pace without your feet spinning too fast. Note. If you always want to go fast on smooth roads, a road bike might be worth considering as an alternative.

1) Only change gears while moving – do not attempt to change gears while parked or inside the vehicle. In that case, the device cannot be changed. Worse, it can cause damage.
How To Shift Road Bike Gears: Shimano, Sram And Camp
2) It’s up to you to change the machine tool. This can be one of his two methods: his two buttons near the brake pedal (the triggers), or the shifters built into the grips (such as Shimano Revoshift).
3) It is important to know ahead of time what the slope will be. If you see a steep climb, be prepared to change gears (etc.).
You’ll be faster on your feet, but you won’t have to climb hills as much as in “high gear”.
“Gear 1” is the lowest gear and he is in 1st gear when the chain is on the largest cog (closest to the rear wheel).
Your Mountain Bike Gear Options Explained
Use “long gear” when walking on flat or gravel roads or when biking in the mountains.
Every time you pedal, you can go farther than you would in a lower gear. Trying to circle a hill in a low gear will spin your legs and tire your muscles quickly.
The top gear, gear 7, is commonly known as “top gear”. When the chain is on the smallest cog (farthest from the rear wheel), it is in 7th gear.

Getting the gears right on a 7-speed bike takes a little practice. Do this and you’ll see it’s a real advantage. You can go around steep slopes and move to the other side faster than without it.
How Many Speeds Do I Need On My Bike
Remember the trigger is on your wrist (whether it’s a small trigger or a rotation)
Road bike gears explained, 21 speed bike gears explained, mountain bike gears explained, 24 speed bike gears explained, gears explained, 7 speed bike gears explained, hybrid bike gears explained, 10 speed bike gears explained, racing bike gears explained, carrera bike gears explained, shimano bike gears explained, 18 speed bike gears explained